Context and objectives
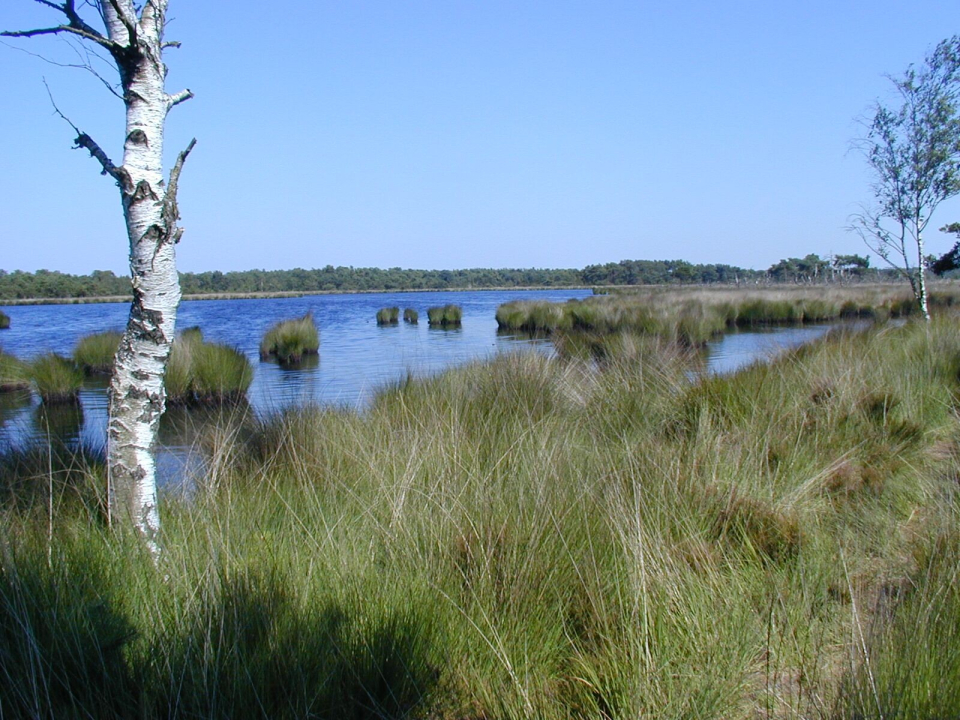
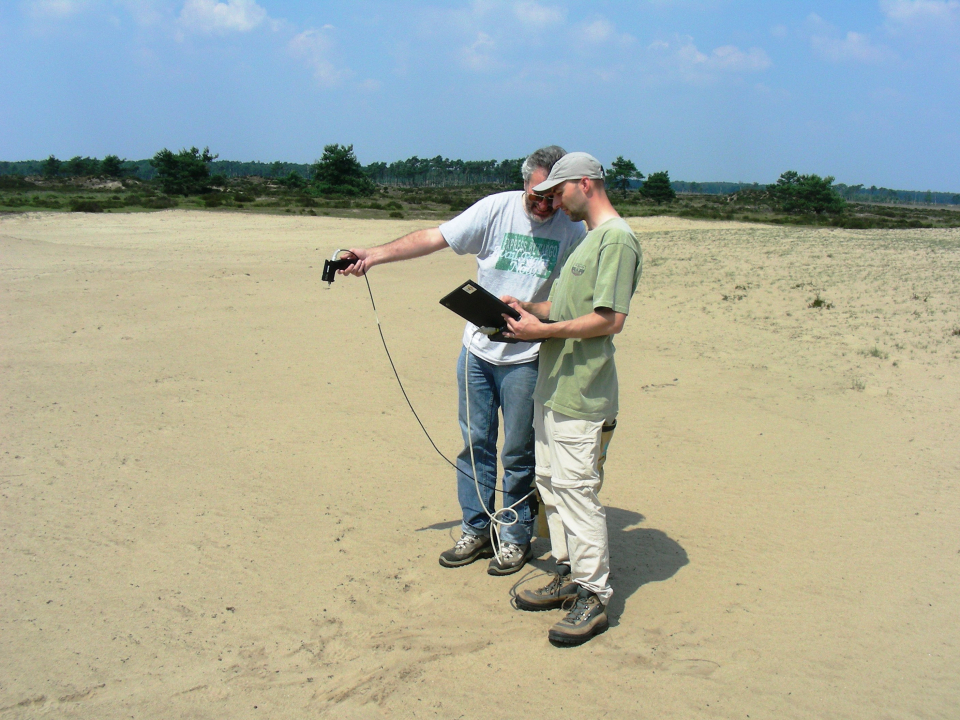
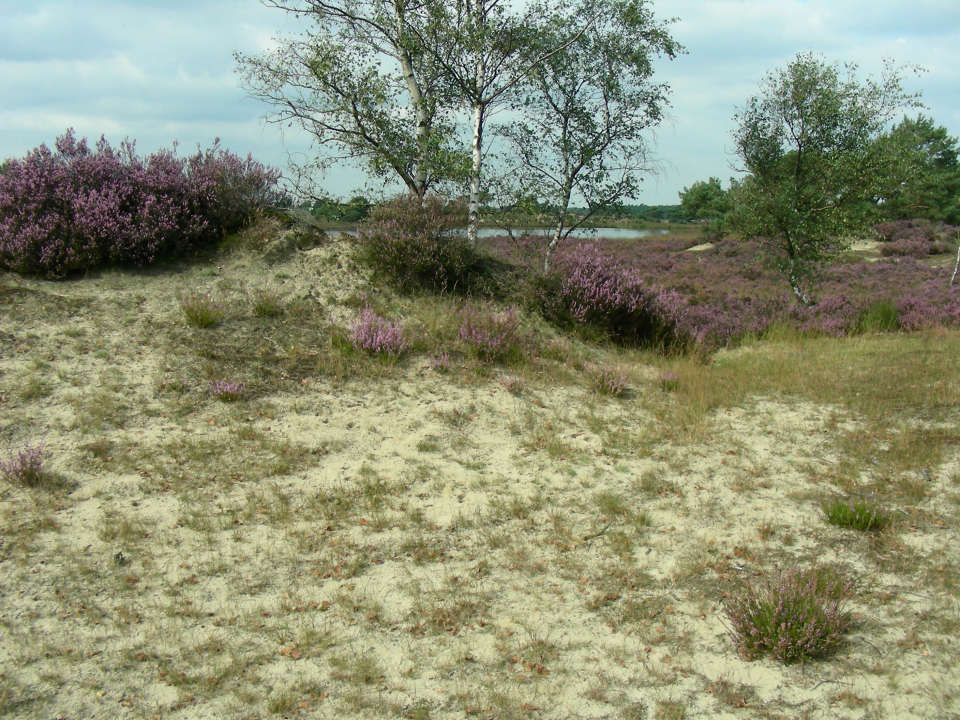
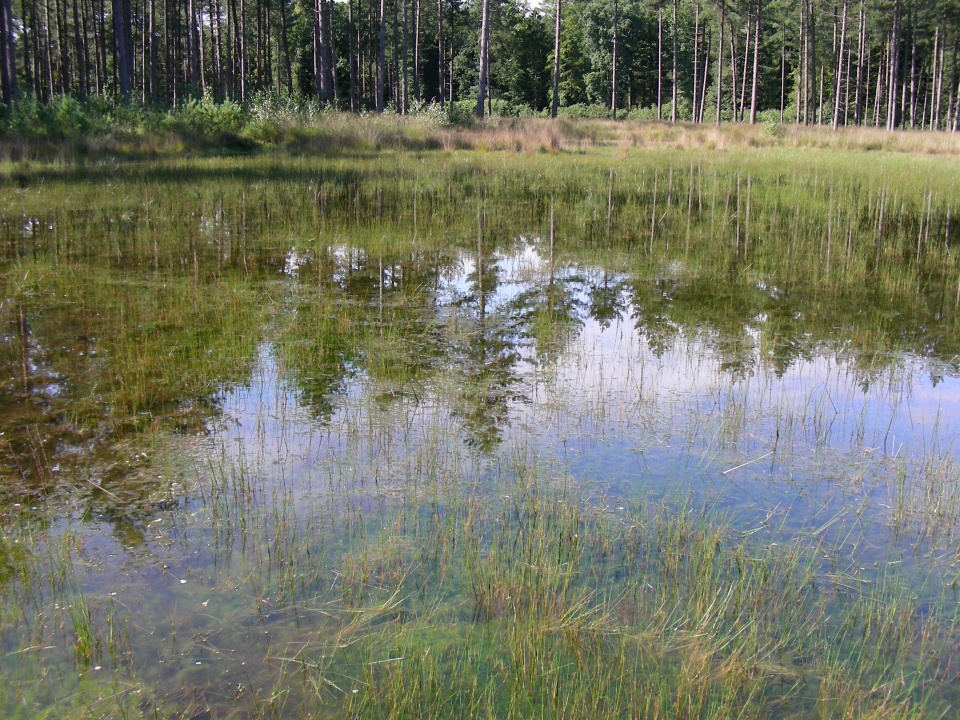
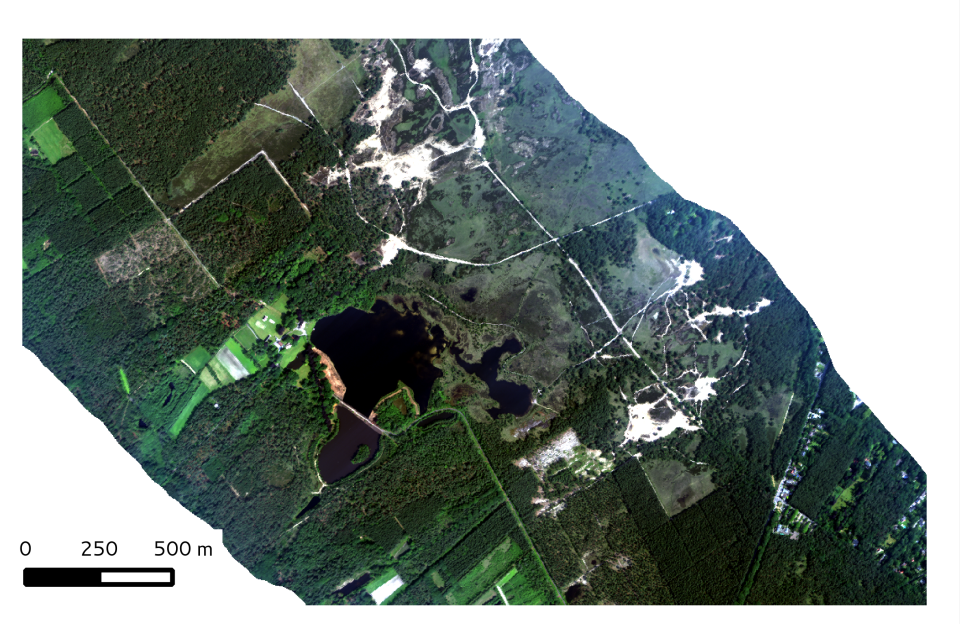
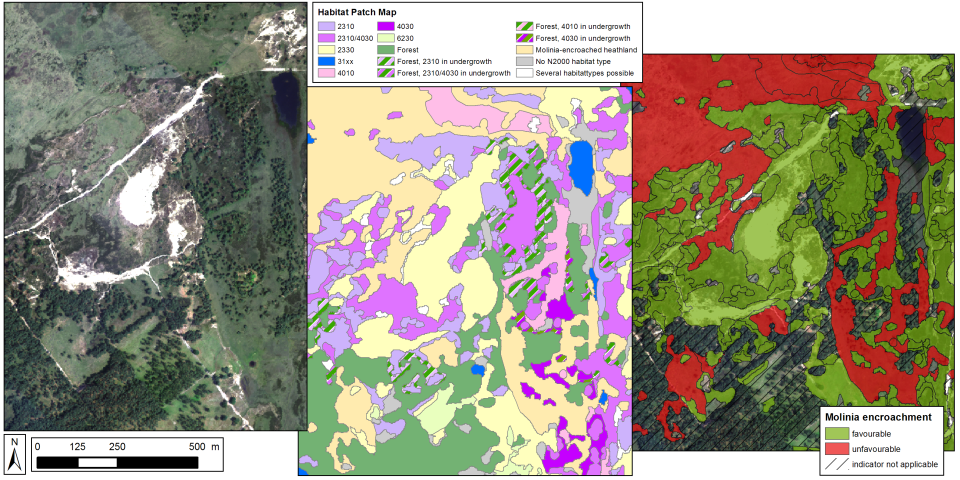
In Europe, the main regulations for biodiversity protection are found in the Habitats and Birds Directive, which provide the legal basis of the Natura 2000 network. To meet the reporting needs of these Directives, detailed, reliable and up-to-date habitat distribution maps are needed that stretch further than merely attributing a vegetation patch to a habitat type. Remote sensing methods can be employed to support these needs, but existing data and classification methods fall short of the purposes of habitat reportage in several aspects: (a) the issue of habitat structure which is most important for assessing habitat quality, has not been addressed; (b) most methods are directed at mapping vegetation species/types, and not at (Natura 2000) habitat patches; (c) most existing remote sensing methodologies have not been tested vigorously for operational purposes. The overall objective of the project was to provide a state-of-the-art classification framework that can be used as a tool that allows better status reporting on habitats using remote sensing data.