The Copernicus Programme is a civil programme building on the existing national and European capacities, as well as ensuring continuity with the activities achieved under the predecessor programme Global Monitoring for Environment and Security (GMES). The programme is implemented by the European Commission in partnership with the European Space Agency (ESA), EU Member States, EU Agencies and other international partners.
The programme is structured around three main pillars:
COPERNICUS SPACE COMPONENT
Space Segment
The Space Segment is made up of the Sentinel satellites which are dedicated to specific tasks such as monitoring land use, air quality and ocean currents. The Sentinel satellites are developed by ESA on behalf of the European Union (EU) and its Member States. They supply remote sensing data of the Earth, delivering key operational services related to environment and security. The Sentinels are currently being developed for the specific needs of the Copernicus programme. Sentinel-1, -2, -3 and -6 are dedicated satellites, while Sentinel-4 and -5 are instruments onboard EUMETSAT’s weather satellites. Sentinel-5P, which is a precursor to Sentinel-5, is also a dedicated satellite.
The Sentinels provide high-resolution photographs of land, provide air quality data and measure the composition of our atmosphere. The most recent Sentinel, Sentinel-6A, was launched in 2020. It provides extremely precise measurements of sea level rise across the globe.
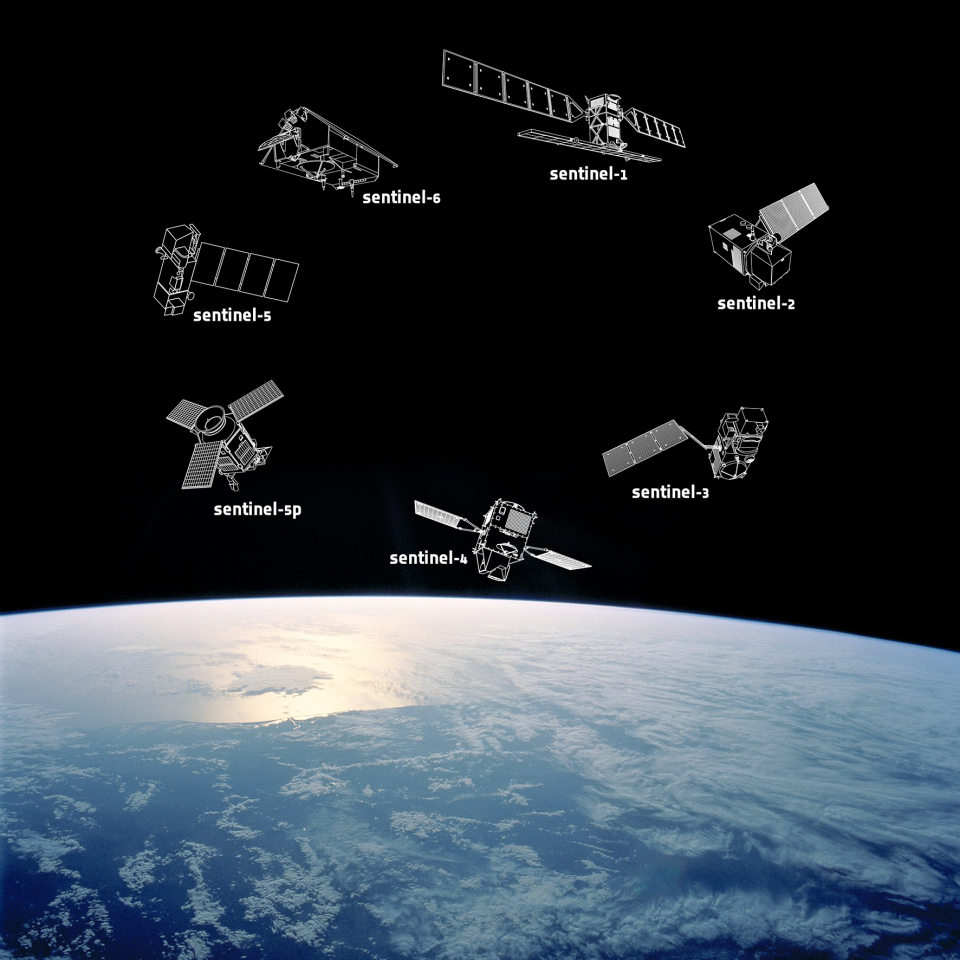
Copernicus Sentinels – a family portrait
Ground Segment
The Ground Segment is responsible for the acquisition, processing and dissemination of data from the Sentinel satellites. The Copernicus Ground Segment is composed of the Core Ground Segment, which is under the responsibility of ESA, complemented by the Sentinel Collaborative Ground Segment and the Contributing Missions Ground Segments. The Sentinel Collaborative Ground Segment was introduced with the aim of exploiting the Sentinel missions even further.
The Sentinel Collaborative Ground Segment is a network of ground-based facilities that are used to acquire, process and distribute data from the Sentinel satellites. The Collaborative Ground Segment is composed of several elements including the Collaborative Data Hub (CDH), the International Access Hub (IAH), the Copernicus Services Data Hub (CSDH) and the National Mirror Sites (NMS). The CDH is a centralised hub that provides access to Sentinel data and products to users worldwide. The IAH provides access to Sentinel data and products to users outside Europe. The CSDH is a centralised hub that provides access to Copernicus services data and products to users worldwide. The NMS are national mirror sites that provide access to Sentinel data and products to users within their respective countries.
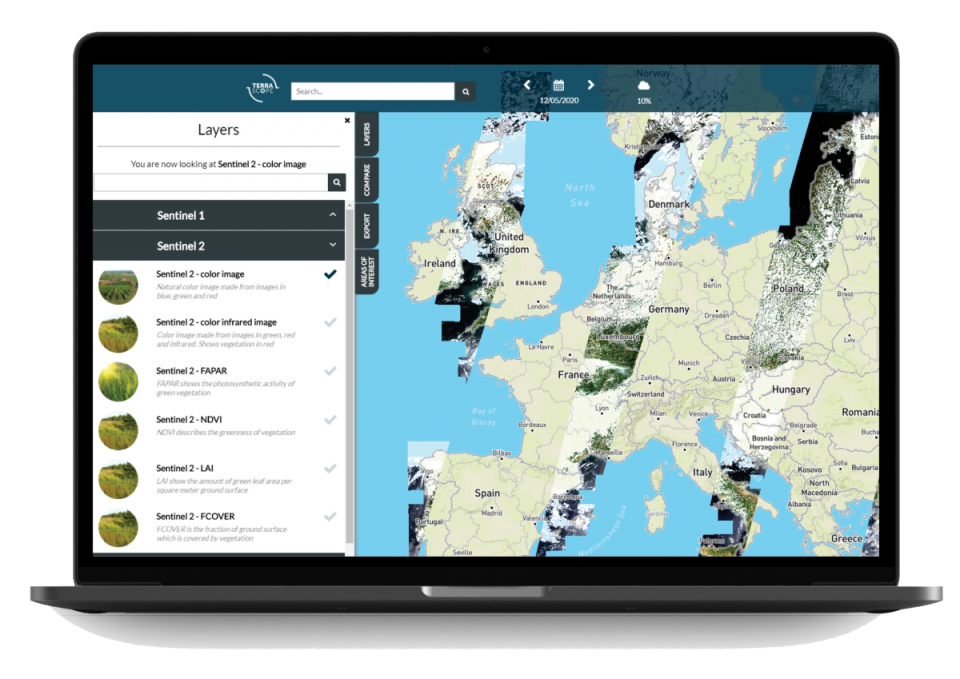
Terrascope, the Belgian Collaborative Ground Segment
The Belgian contribution to the Collaborative Ground Segment is Terrascope. It provides access to Sentinel data and products as well as other Earth observation data. Terrascope also provides processing tools that allow users to process and analyse the data.
More information on Terrascope
COPERNICUS SERVICES
The programme provides six services: Atmosphere Monitoring Service (CAMS), Climate Change Service (C3S), Emergency Management Service (EMS), Land Monitoring Service (CLMS), Marine Environment Monitoring Service (CMEMS) and Security Service (Copernicus Security Service). These services are based on satellite data and in-situ measurements, which are processed and analyzed by specialized centers located across Europe.
The Copernicus Programme has been instrumental in providing data for various applications such as agriculture, forestry, fisheries, urban planning, air quality monitoring, disaster management and climate change mitigation. The programme has also been used to monitor wildfires, floods, oil spills and other natural disasters.

An overview of the Copernicus Services
IN SITU COMPONENT
Copernicus services rely on data from in situ monitoring networks (e.g. ground based weather stations, ocean buoys and air quality monitoring networks) to provide robust integrated information and to calibrate and validate the data from satellites.
In situ data are an essential and integrated part of Copernicus, and are used extensively every day by the Copernicus services and the space component to produce products, and deliver services that are requested by end users. They are also used for the calibration and validation of satellite missions.