Published on 31 August 2023
These include several Heritage Missions, such as ESA’s European Remote Sensing satellite (ERS) programme – which was active between 1991 and 2011 – and the agency’s Envisat satellite, which launched in 2002 and delivered 10 years of data.
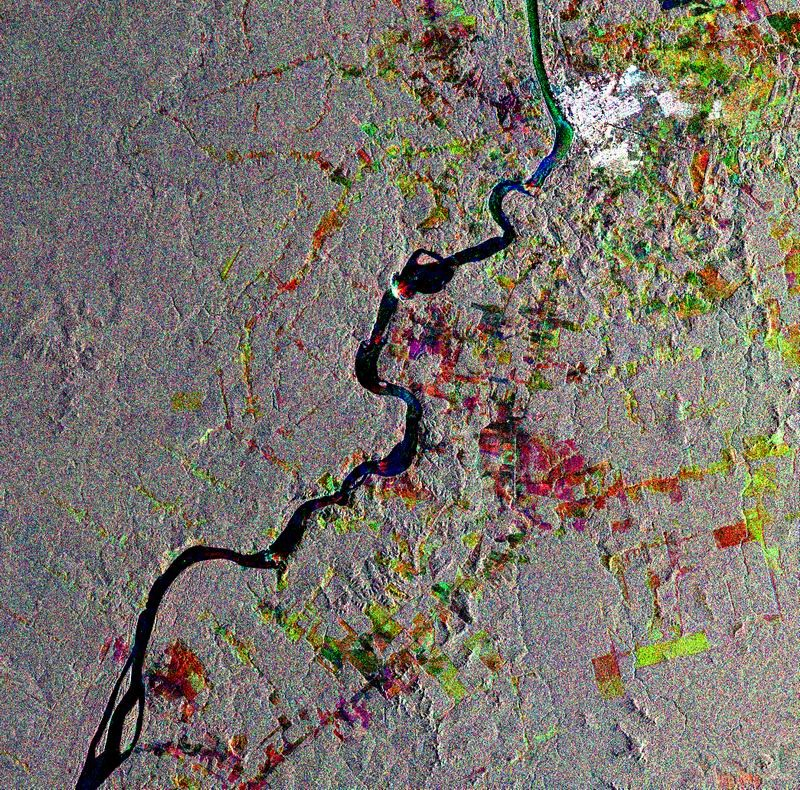

ERS-2 monitors changes in forest cover in Brazil
Data from instruments carried by ERS are used to map forest cover, detect deforestation, help estimate biomass and carbon storage – and even track the impact of forest fires.
Envisat hosted a suite of instruments, with its Medium Resolution Imaging Spectrometer (MERIS) and its Advanced Synthetic Aperture Radar (ASAR) sensor enabling detailed analyses of different aspects of forest dynamics.
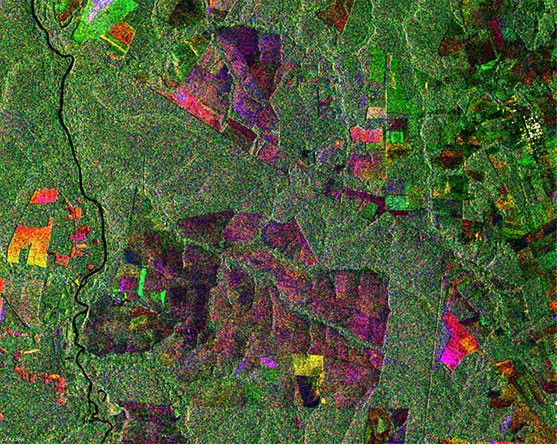
Envisat tracks deforestation in Brazil
Using these sensors, Envisat and ERS delivered valuable information on deforestation in the Amazon basin in the 1990s and 2000s.
These data – as well as observations covering other regions – are used in combination with measurements from more recent missions, enabling continuous analyses that are improving long-term understanding of how forests are changing, thus spurring action to protect them.
Data from ESA’s Heritage Missions are maintained, made accessible, and continuously improved through ESA’s Heritage Space programme.
Source:
European Space Agency. (2023). Tracking the world’s forests from space. Earth Online.