Publié le 25 avril 2023
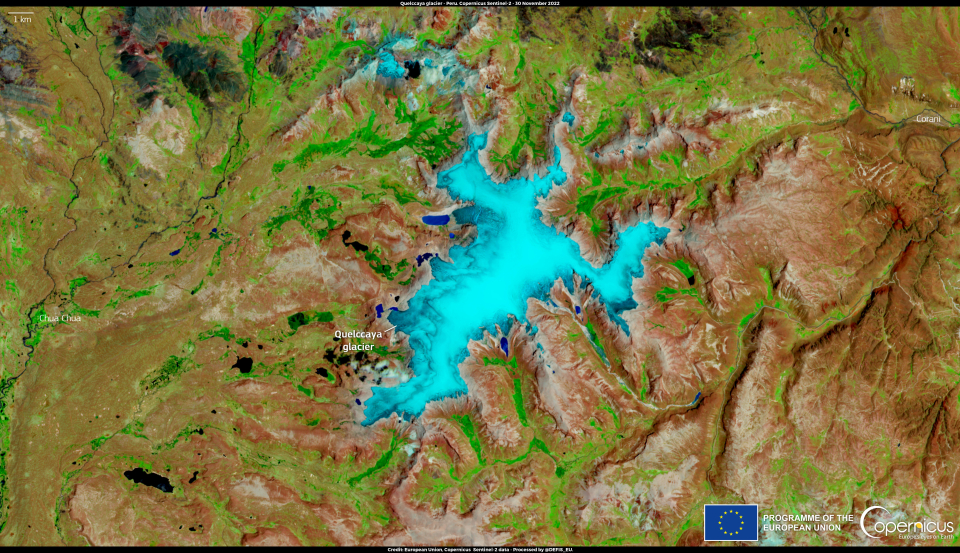
The Quelccaya glacier in the Andes of Peru can be seen in this image, captured on 30 November 2022 by one of the Copernicus Sentinel-2 satellites.
The Quelccaya glacier, which was once the world's largest tropical ice cap, has been reduced its volume by nearly 50% over the past four decades and is rapidly melting at a rate of about 5% per year as a result of climate change. The decline of the the health of the glacier has had a significant impact on the people of the nearby community, who rely on it for their water supply and livelihoods.
The Copernicus satellites play a crucial role in the monitoring of glaciers worldwide, providing essential information which helps researchers and decision-makers develop effective strategies for addressing the challenges stemming from climate change.