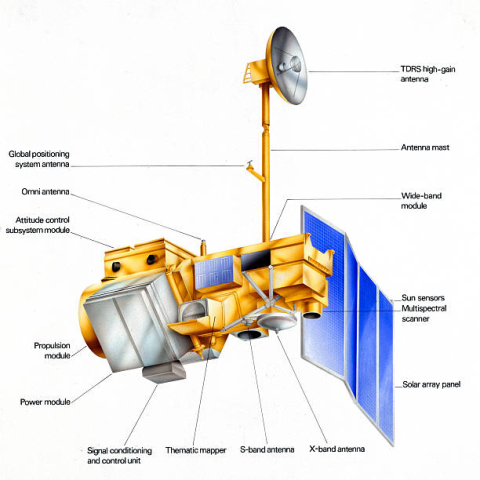
Satellite characteristics
Launch Date - End 1 March 1984 - 5 June 2013
État Decommissioned
Orbit type polar, sun-synchronous
Altitude 705
Orbit inclination 98.2
Equatorial crossing time 09:45:00
Orbit period 99
Satellite family: LANDSAT
The Landsat Program is a series of Earth-observing satellite missions jointly managed by NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey. Since 1972, Landsat satellites have collected information about Earth from space. This science, known as remote sensing, has matured with the Landsat Program.Landsat 1 (formerly named Earth Resources Technology Satellite -ERTS-1-) was launched on July 23, 1972. The launches of Landsat 2, Landsat 3, and Landsat 4 followed in 1975, 1978, and 1982, respectively.
When Landsat 5 launched in 1984, no one could have predicted that the satellite would continue to deliver high quality, global data of Earth’s land surfaces for 28 years and 10 months, officially setting a new Guinness World Record for "longest-operating Earth observation satellite." Landsat 6 failed to achieve orbit in 1993.
Landsat 7 successfully launched in 1999 and, along with Landsat 8, which launched in 2013, continues to provide daily global data. Landsat 9 is planned to launch in late 2020.
More information : The Landsat Mission (USGS)
Sensor characteristics
| Sensor name | MSS1 (Multispectral Scanner 1) |
|---|---|
| Sensor short description | These scanners were identical to those on the first two Landsat satellites. The only difference was that the four spectral bands were numbered from 1 to 4 since the RBVs were no longer used. Landsat 5’s MSS stopped acquiring data in 1992. |
| Sensor type | Imaging radiometer (Vis/IR) |
| Resolution class | Medium (30 - 300 m) |
| Spatial resolution | 68 m x 83 m |
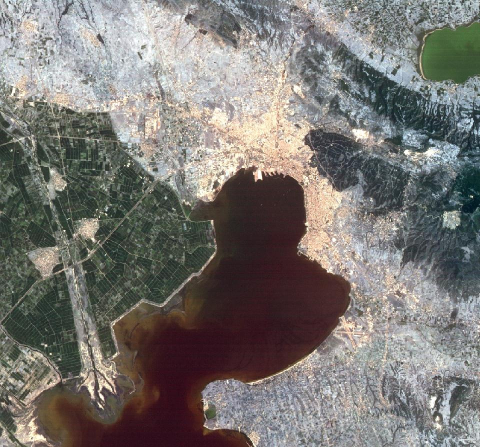
| Spectral bandwidth | Band 1: 0,5 - 0,6 µm - Coastal zones, marine sediments<br> Band 2: 0,6 - 0,7 µm - Roads and urban areas<br> Band 3: 0,7 - 0,8 µm - Plant studies and mapping of earth/water boundaries<br> Band 4: 0,8 - 1,1 µm - Plant studies and mapping of earth/water boundaries |
| Swath width (at nadir) | 185 km |
| Sensor name | TM (Thematic Mapper) |
|---|---|
| Sensor short description | These high-resolution scanners have seven spectral bands and always cover a 185 x 185 km area. |
| Sensor type | Imaging radiometer (Vis/IR) |
| Resolution class | High (5 - 30 m) |
| Spatial resolution | 30m (VIS & IR) 120m (Thermal) |
| Spectral bandwidth | Band 1: 0,45 - 0,52 µm (blue) - Ground/plants differentiation, coastal zones<br> Band 2: 0,52 - 0,60 µm (green) - Vegetation<br> Band 3: 0,63 - 0,69 µm (red) - Plant species differentiation<br> Band 4: 0,76 - 0,90 µm (near infrared NIR) - Biomass<br> Band 5: 1,55 - 1,75 µm (short wave infrared SWIR)- Snow/cloud differentiation<br> Band 6: 10,41 - 12,5 µm (thermal)<br> Band 7: 2,08 - 2,35 µm (shortwave infrared SWIR) - Lithology |
| Swath width (at nadir) | 185 km |