Gepubliceerd op 11 april 2022
Straddling the border of southeast Utah and northeast Arizona, Lake Powell is an important reservoir in the Colorado River Basin. The Colorado River, which Lake Powell flows through, was dammed at Glen Canyon in the early 1960s. The lake provides water to approximately 40 million people, irrigates over 2.2 million hectares of land and has the capacity to generate more than 4200 megawatts of hydropower electricity.
In mid-March 2022, Lake Powell’s elevation dropped to an astonishing 1074 m above sea level – the lowest the lake has been since it was filled in 1980. This drastic drop in water levels is documented in natural-colour images captured by the Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission.
The area pictured below shows the surface area changes of the reservoir near Bullfrog Marina, approximately 90 km north from Glen Canyon Dam, between March 2018 and March 2022. Dry conditions and falling water levels are unmistakable in the image captured on 18 March 2022, compared to the 2018 shoreline outlined in the image in yellow.
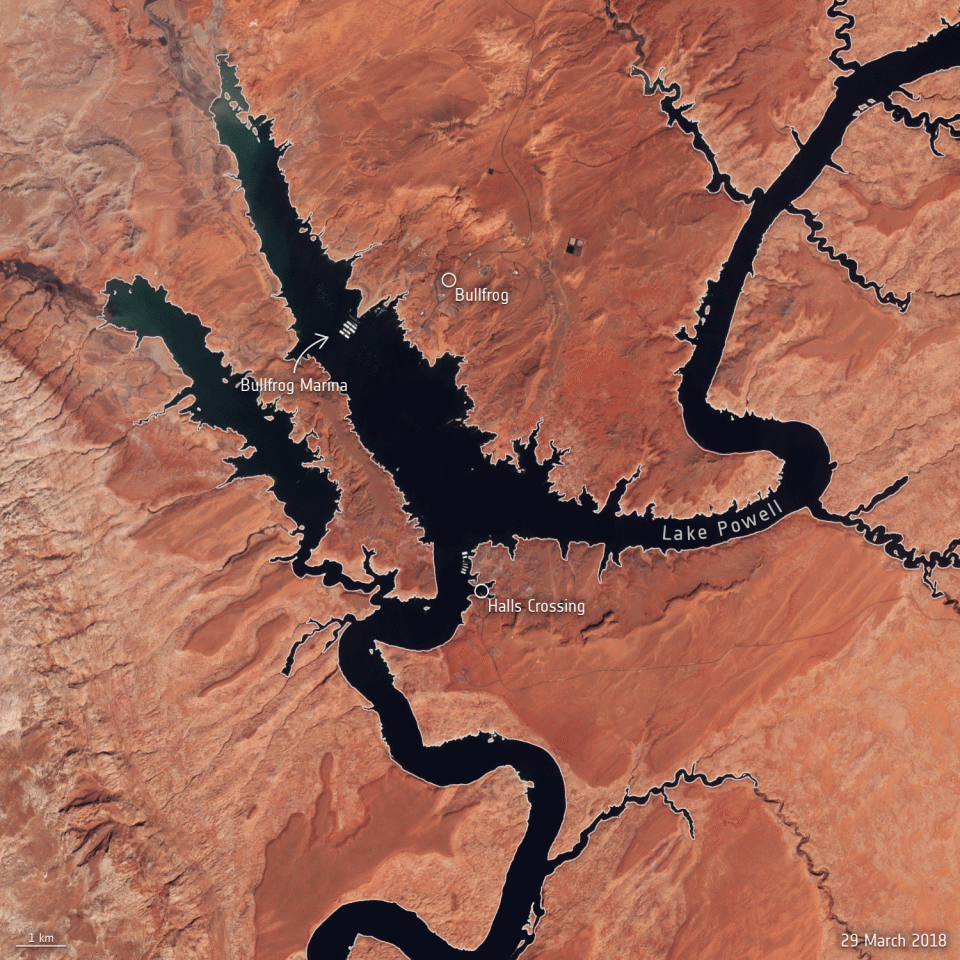
Surface area changes of Lake Powell
Click here to view this image at full resolution
The drop in water levels comes as hotter temperatures and falling water levels left a smaller amount of water flowing through the Colorado River. The peak inflow to Lake Powell occurs in mid-to-late spring, as the winter snow in the Rocky Mountains melts.
The line graph shows the drastic drop in average water levels in March since 2000, when Lake Powell was at around 1120 m elevation. The current elevation is just a few meters from what is considered the ‘minimum power pool’ – the level at which Glen Canyon Dam is able to generate hydroelectric power. If Lake Powell drops even more, it could soon hit a ‘deadpool’ where water will likely fail to flow through the dam and onto the nearby Lake Mead.
Read the rest of the article
over on the ESA Observing the Earth website