Satellite characteristics
Launch Date - End 21 April 1995 - 6 July 2011
Status Decommissioned
Orbit type Sun-synchronous polar orbit
Altitude 780
Orbit inclination 98.5
Equatorial crossing time 10:30:00
Orbit period 100
Satellite family: ERS (European Remote-Sensing Satellite)
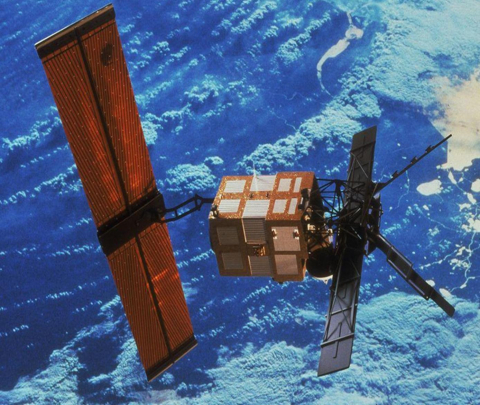
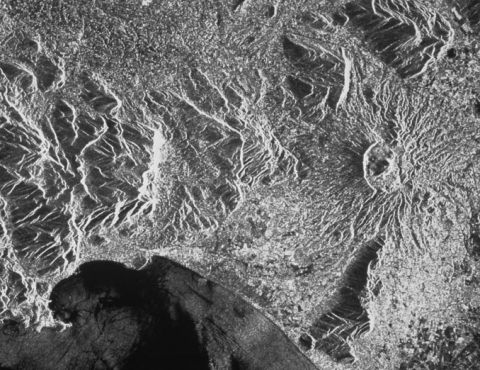
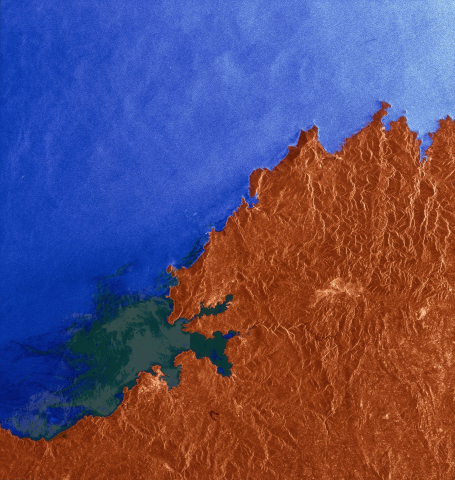
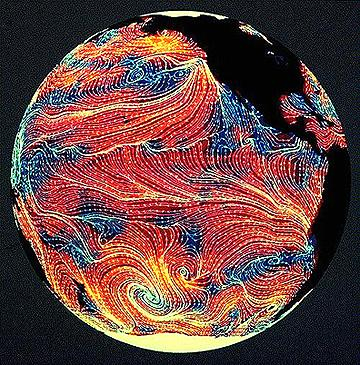
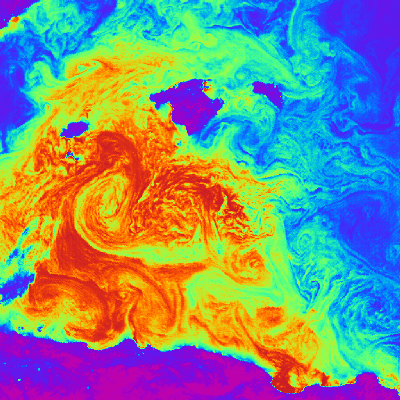
The European Remote Sensing satellite ERS-1, launched in 1991, carried a comprehensive payload including an imaging synthetic aperture radar, a radar altimeter and other powerful instruments to measure ocean surface temperature and winds at sea. ERS-2, which overlapped with ERS-1, was launched in 1995 with an additional sensor for atmospheric ozone research.
At their time of launch the two ERS satellites were the most sophisticated Earth observation spacecraft ever developed and launched by Europe. These highly successful ESA satellites collected a wealth of valuable data on Earth’s land surfaces, oceans, and polar caps and were called upon to monitor natural disasters such as severe flooding or earthquakes in remote parts of the world.
Both ERS satellites were built with a core payload of two specialised radars and an infrared imaging sensor. The two were designed as identical twins with one important difference: ERS-2 included an extra instrument to monitor ozone levels in the atmosphere.
Shortly after the launch of ERS-2 in 1995 ESA decided to link the two satellites in the first ‘tandem’ mission which lasted for nine months. During this time the increased frequency and level of data available to scientists offered a unique opportunity to observe changes over a very short space of time, as both satellites orbited Earth only 24 hours apart.
The ERS-1 mission ended on 10 March 2000 and ERS-2 was retired on 05 September 2011.
Sensor characteristics
| Sensor name | AMI SAR (Active Microwave Instrument Synthetic Aperture Radar) |
|---|---|
| Sensor short description | |
| Sensor type | Imaging microwave radar |
| Resolution class | High (5 - 30 m) |
| Swath width (at nadir) | 100 km |
| Max look angle | 23 ° |
| Sensor name | AMI WS (Active Microwave Instrument Wind Scatterometer) |
|---|---|
| Sensor short description | |
| Sensor type | Imaging microwave radar |
| Resolution class | Very Low (> 1 km) |
| Swath width (at nadir) | 500 km |
| Max look angle | 47 ° |
| Sensor name | ATSR IRR (Along Track Scanning Radiometer Infra-Red Radiometer) |
|---|---|
| Sensor short description | |
| Sensor type | Imaging radiometer (Vis/IR) |
| Resolution class | Very Low (> 1 km) |
| Swath width (at nadir) | 500 km |
| Max look angle | 47 ° |
| Sensor name | ATSR MWS (Along Track Scanning Radiometer Microwave Sounder) |
|---|---|
| Sensor short description | |
| Sensor type | Imaging microwave radar |
| Resolution class | Very Low (> 1 km) |
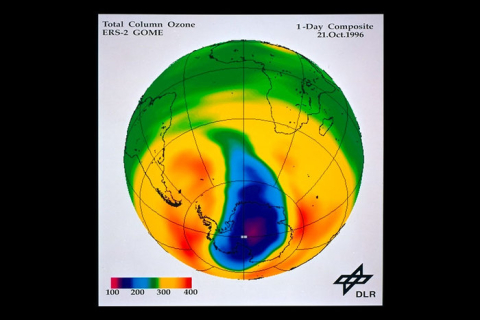
| Sensor name | GOME (Global Ozone Monitoring Experiment) |
|---|---|
| Sensor short description | |
| Sensor type | Atmospheric instrument |
| Resolution class | Very Low (> 1 km) |
| Swath width (at nadir) | 960 km |
| Max look angle | 31 ° |
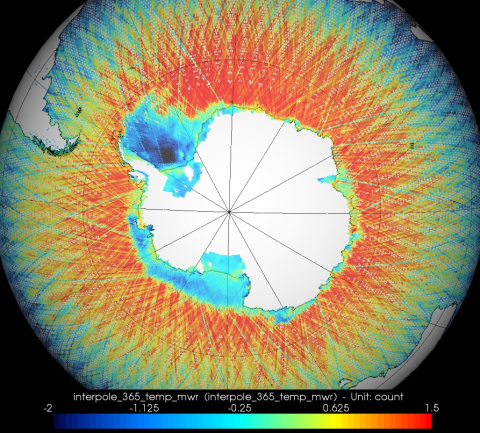
| Sensor name | MWR (Microwave Radiometer) |
|---|---|
| Sensor short description | MWR is a nadir-viewing, two-channel Dicke-type radiometer (passive sensor). The main objectives of MWR is the measurement of atmospheric humidity as supplementary information for tropospheric path correction of the RA-2 signal, which is influenced by the integrated atmospheric water content and by liquid water. In addition, MWR measurements are useful for the determination of surface emissivity and soil moisture of land, for surface energy budget estimations, investigations to support atmospheric studies, and for ice characterization. |
| Sensor type | Imaging radiometer (passive microwave) |
| Resolution class | Very Low (> 1 km) |
| Spectral bandwidth | 23.8 (K-band) and 36.5 (Ka-band) GHz |
| Swath width (at nadir) | 20 km |
| Max look angle | 47 ° |
| Sensor name | RA (Radar Altimeter) |
|---|---|
| Sensor short description | |
| Sensor type | Radar altimeter |
| Resolution class | Very Low (> 1 km) |