PACE will help us better understand our ocean and atmosphere by measuring key variables associated with cloud formation, particles and pollutants in the air, and microscopic, floating marine life (phytoplankton). These observations will help us better monitor ocean health, air quality, and climate change.
Sensor characteristics
| Sensor name | Ocean Color Instrument (OCI) |
|---|---|
| Sensor short description |
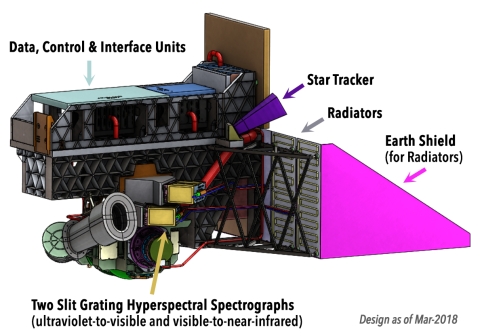
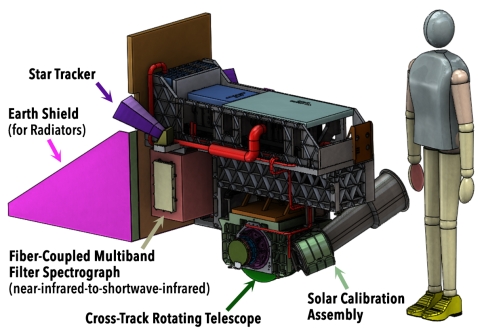
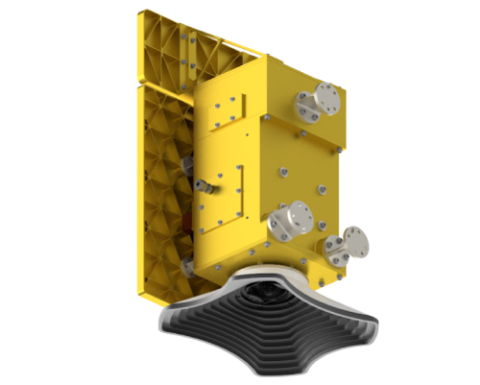
PACE's primary sensor, the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI), is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. The color of the ocean is determined by the interaction of sunlight with substances or particles present in seawater such as chlorophyll, a green pigment found in most phytoplankton species. By monitoring global phytoplankton distribution and abundance with unprecedented detail, the OCI will help us to better understand the complex systems that drive ocean ecology. The OCI is being built at Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC). It will consist of a cross-track rotating telescope, thermal radiators, along with half-angle mirror and solar calibration mechanisms. The OCI's tilt will help avoid sun glint and single science detector design will inhibit image striping. Its signal-to-noise ratios will rival or exceed previous ocean color instruments. The OCI will feature:
|
| Sensor type | Imaging radiometer (Vis/IR) |
| Sensor name | SPEXone Polarimeter |
|---|---|
| Sensor short description | PACE's SPEXone instrument is a multi-angle polarimeter. It measures the intensity, Degree of Linear Polarization (DoLP) and Angle of Linear Polarization (AoLP) of sunlight reflected back from Earth's atmosphere, land surface, and ocean. The focus of the SPEXone development is to achieve a very high accuracy of DoLP measurements, which facilitates accurate characterization of aerosols in the atmosphere. Aerosols are small solid or liquid particles suspended in the air that affect climate directly through interaction with solar radiation. Aerosols affect climate indirectly by changing the micro- and macro-physical properties of clouds. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, aerosols are the largest source of error in quantifying the radiative forcing of climate change. SPEXone will enable measurements of optical and micro-physical properties of aerosols with unprecedented detail and accuracy.
SPEXone is being developed by a Dutch consortium consisting of SRON Netherlands Institute for Space Research (SRON) and Airbus Defence and Space Netherlands (Airbus DS NL), supported by optical expertise from the Netherlands Organisation for Applied Scientific Research. SRON and Airbus DS NL are responsible for the design, manufacturing and testing of the instrument. The scientific lead is in the hands of SRON. SPEXone is a public-private initiative funded by the Netherlands Space Office (NSO), the Netherlands Organization of Scientific Research (NWO), SRON, and Airbus DS NL. SPEXone will feature:
|
| Sensor name | HARP2 Polarimeter |
|---|---|
| Sensor short description | HARP2 (Hyper-Angular Rainbow Polarimeter #2) is a wide angle imaging polarimeter designed to measure aerosol particles and clouds, as well as properties of land and water surfaces. The amount and type of particles in suspension in the atmosphere are relevant to applications pertaining to health effects, cloud life cycle and precipitation, climate, etc. HARP2 will combine data from multiple along track viewing angles (up to 60), four spectral bands in the visible and near infrared ranges, and three angles of linear polarization to measure the microphysical properties of the atmospheric particles including their size distribution, amount, refractive indices and particle shape. HARP2 is a contributed instrument to the PACE mission, designed and built by UMBC's Earth and Space Institute. |