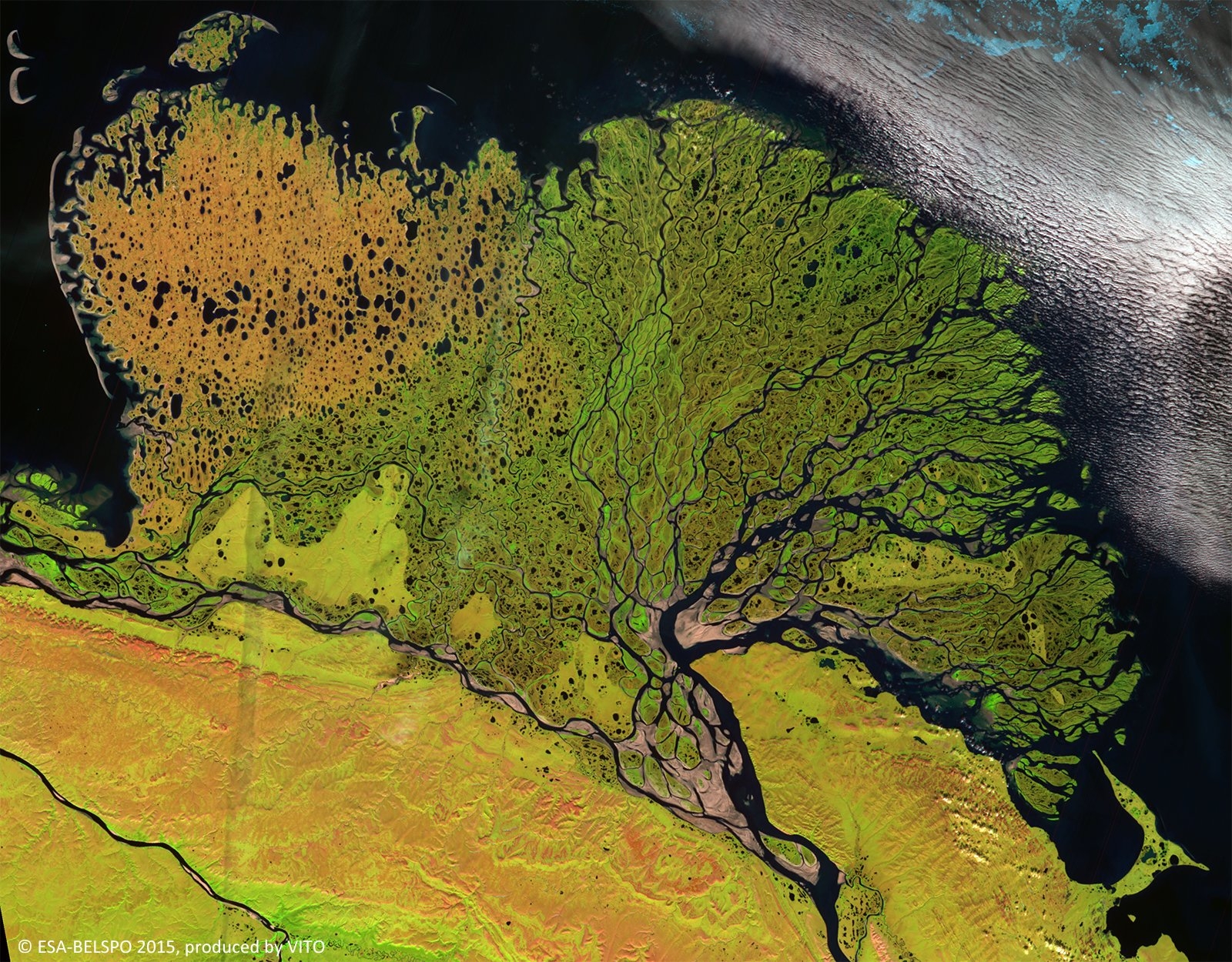
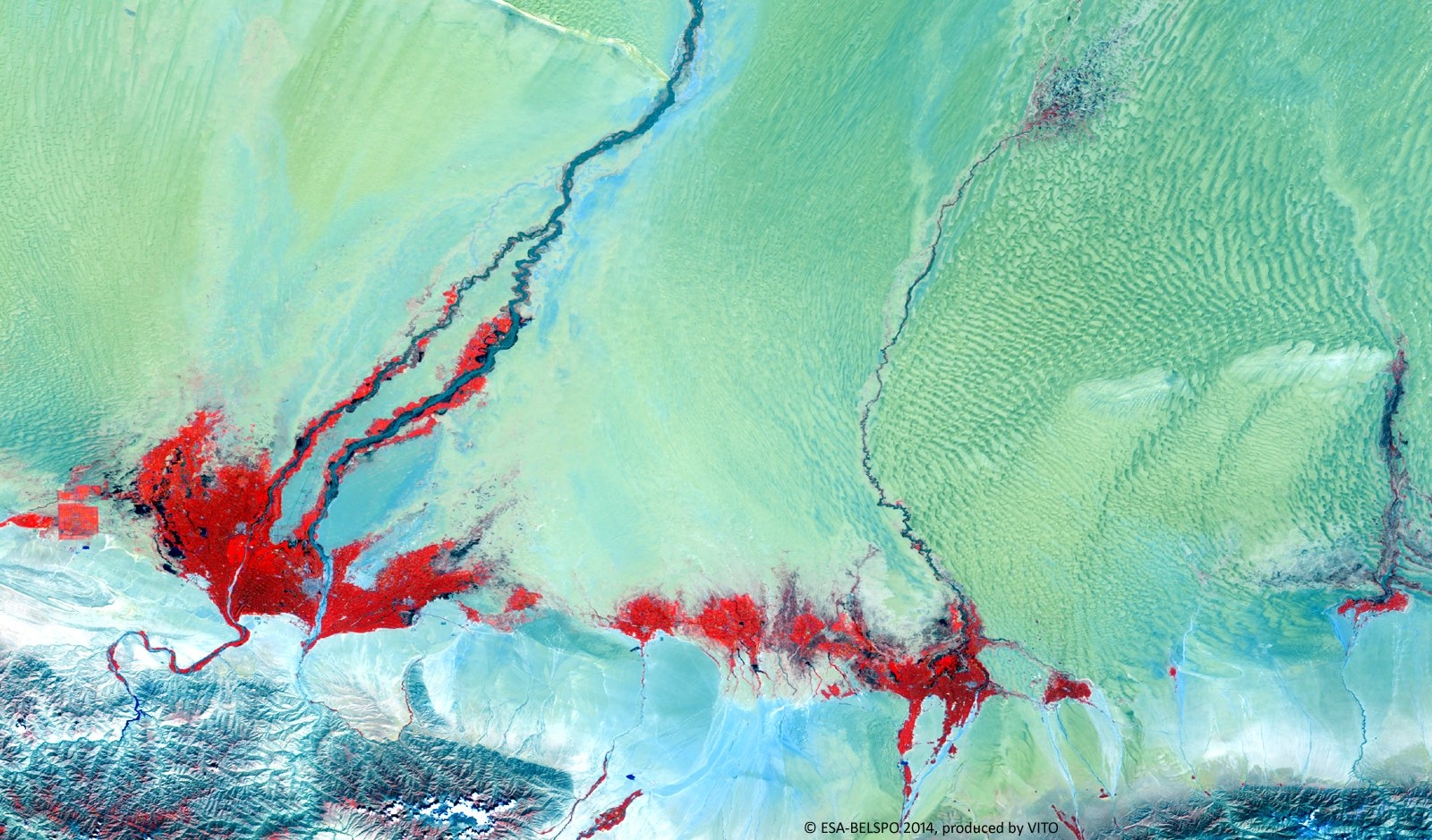
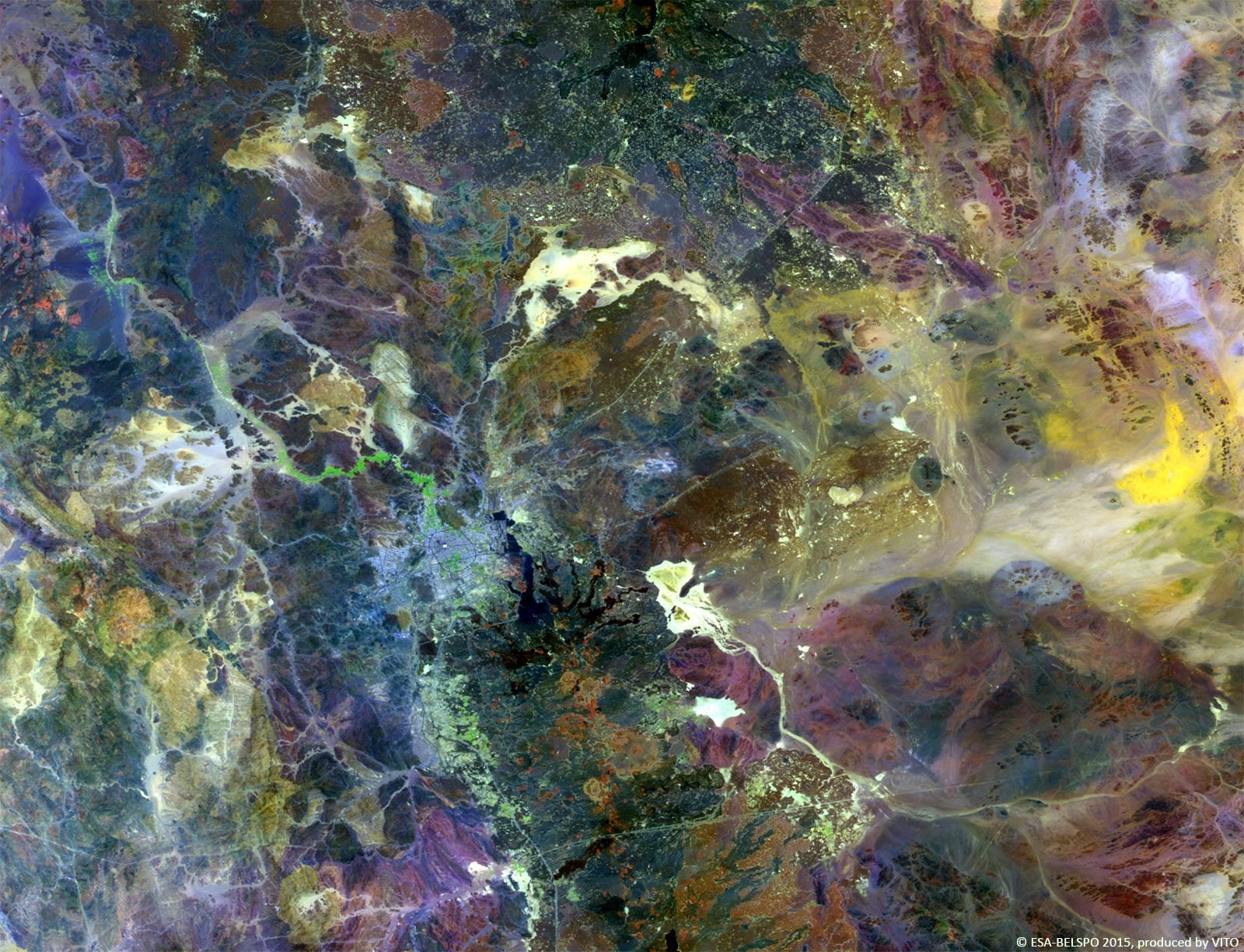
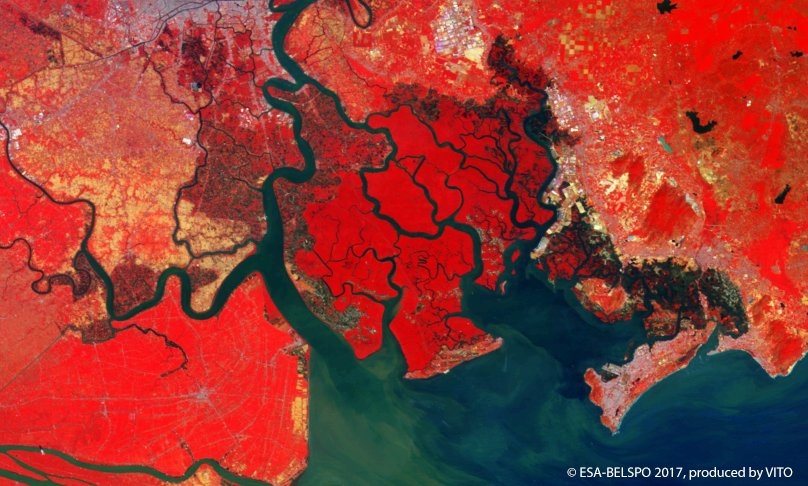
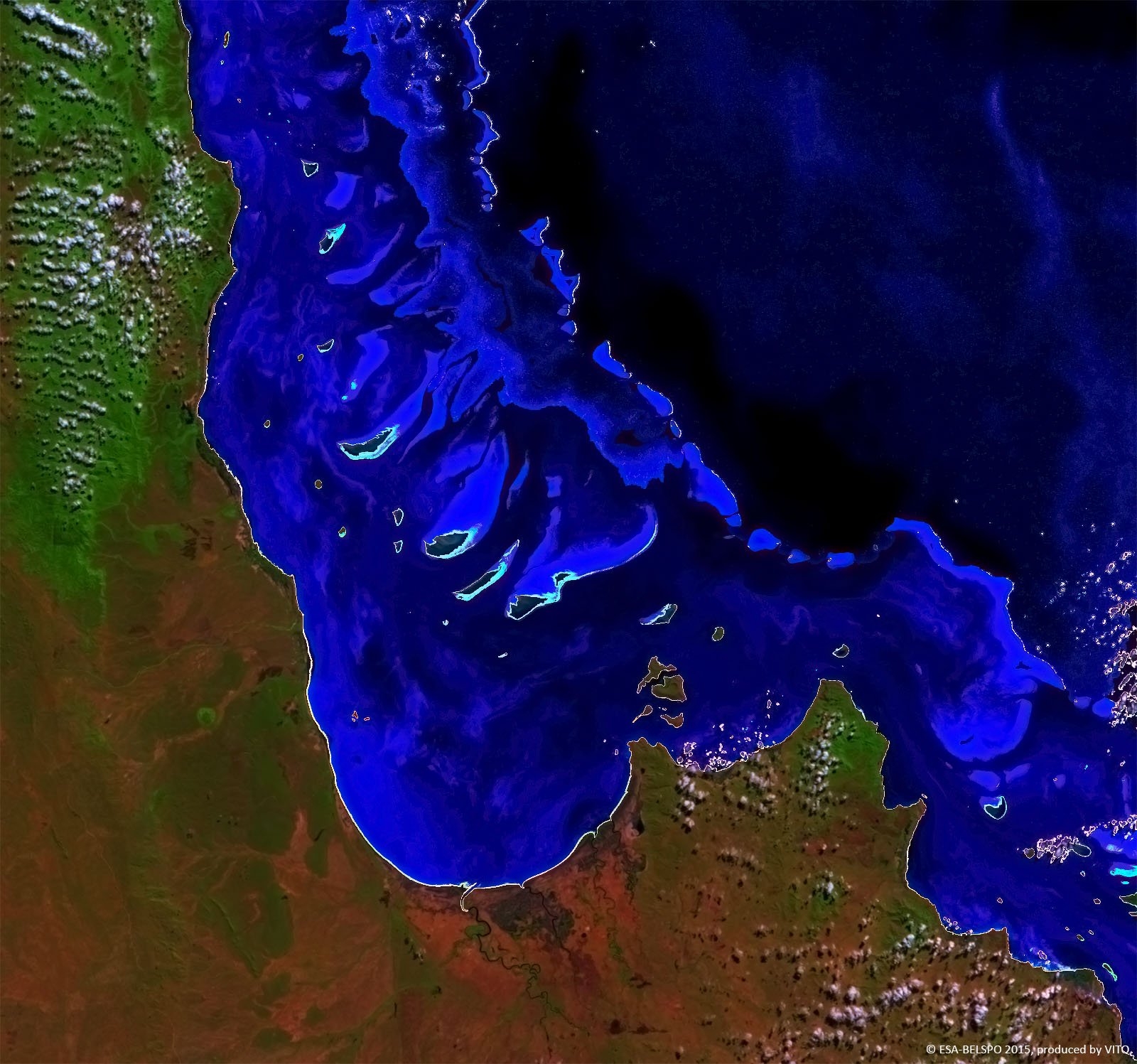
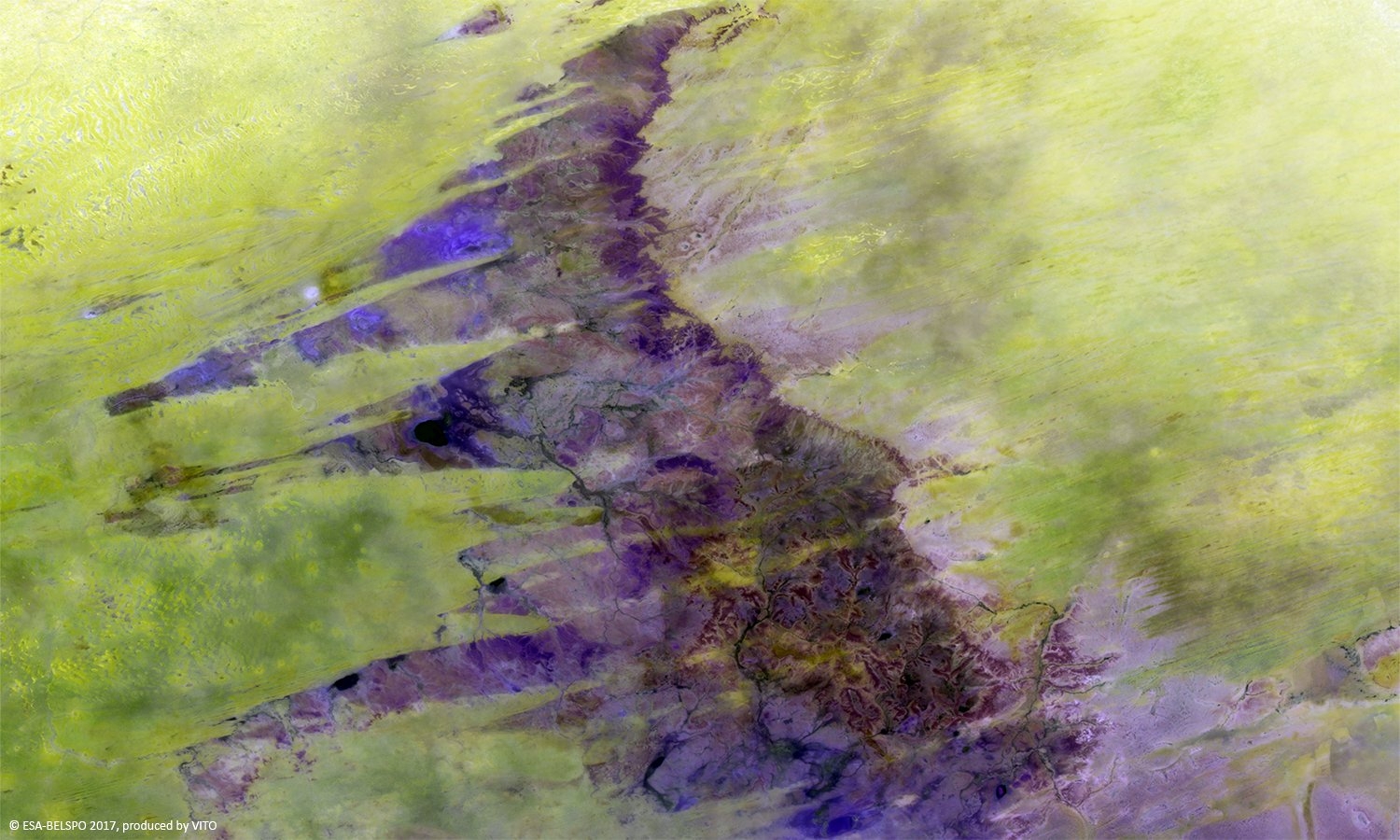
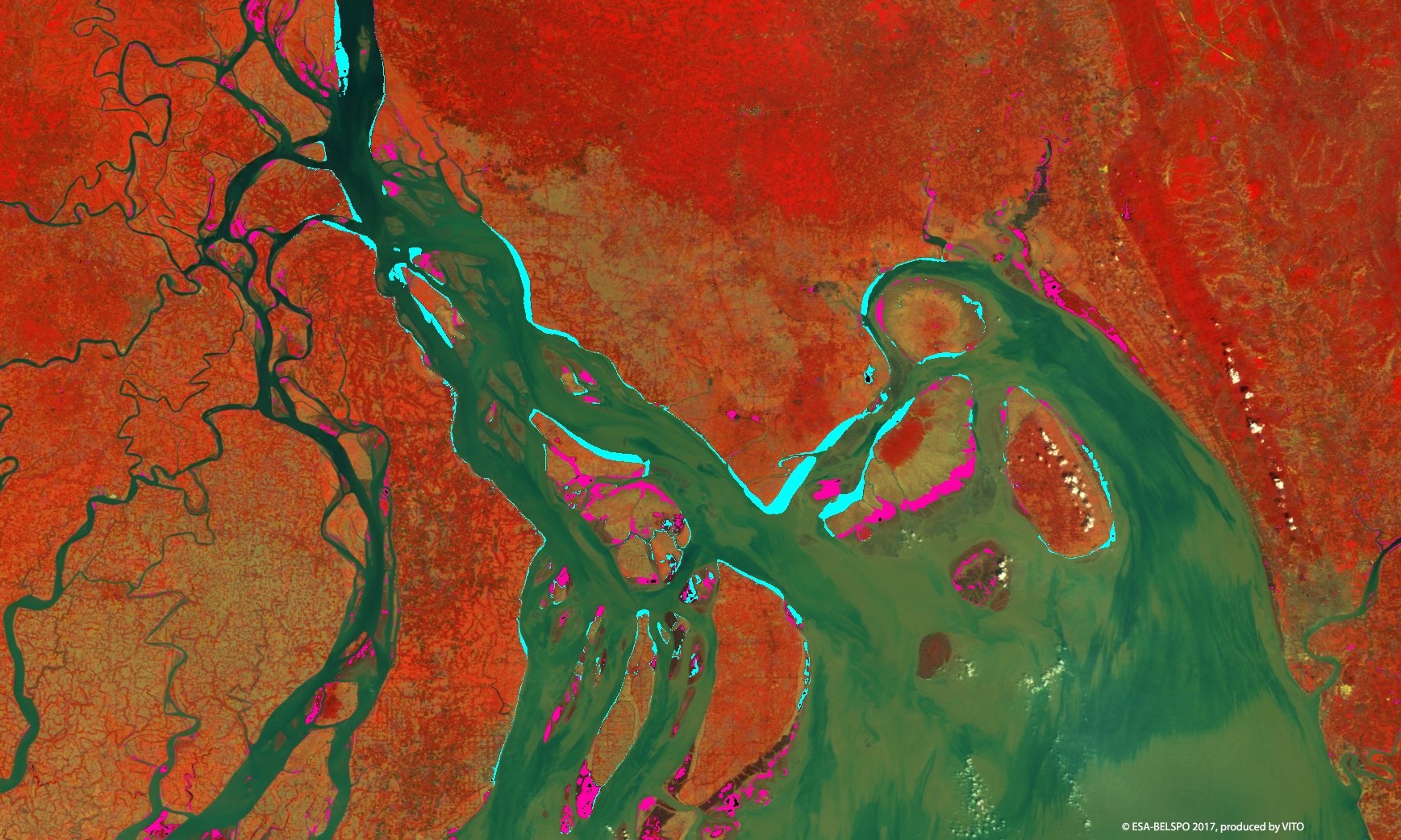
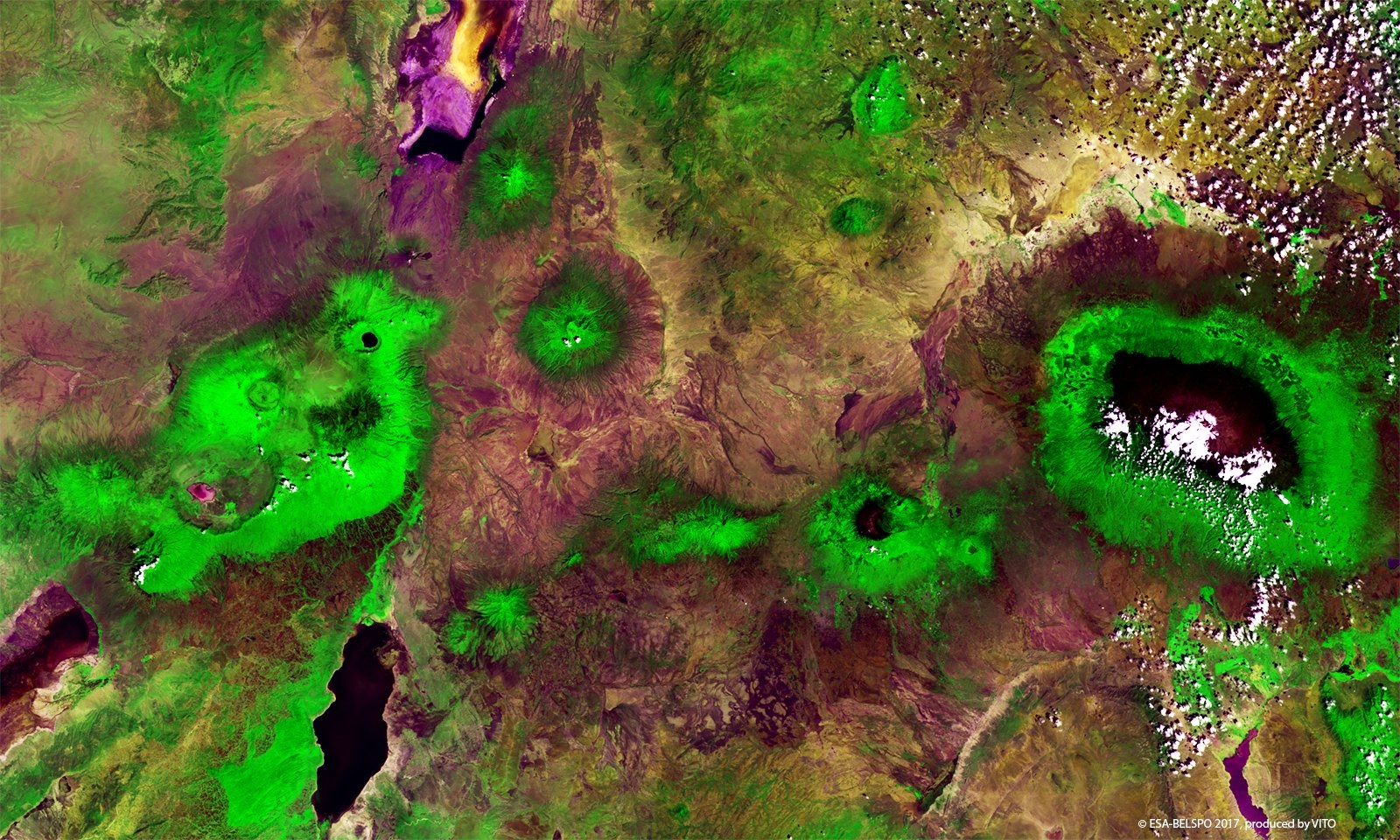
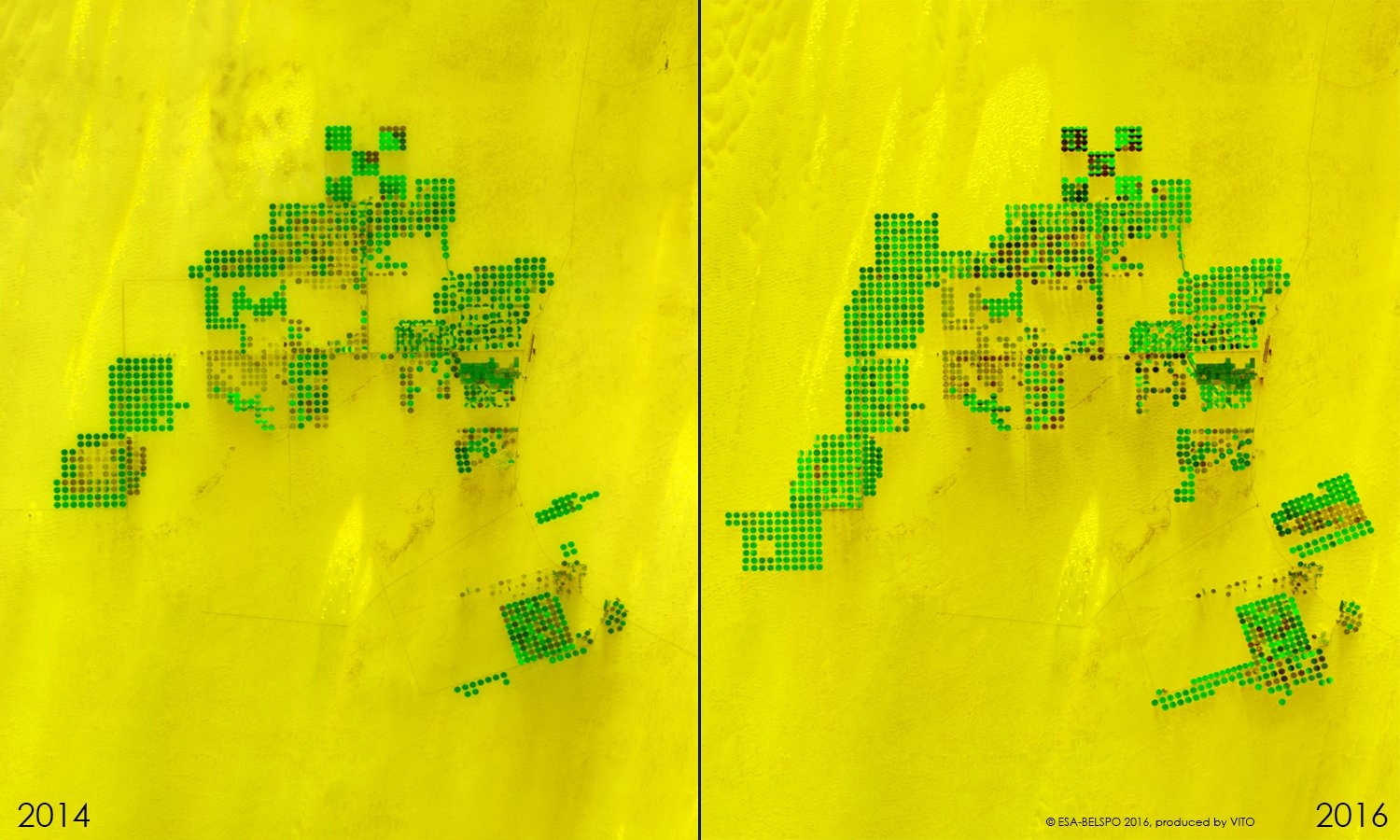
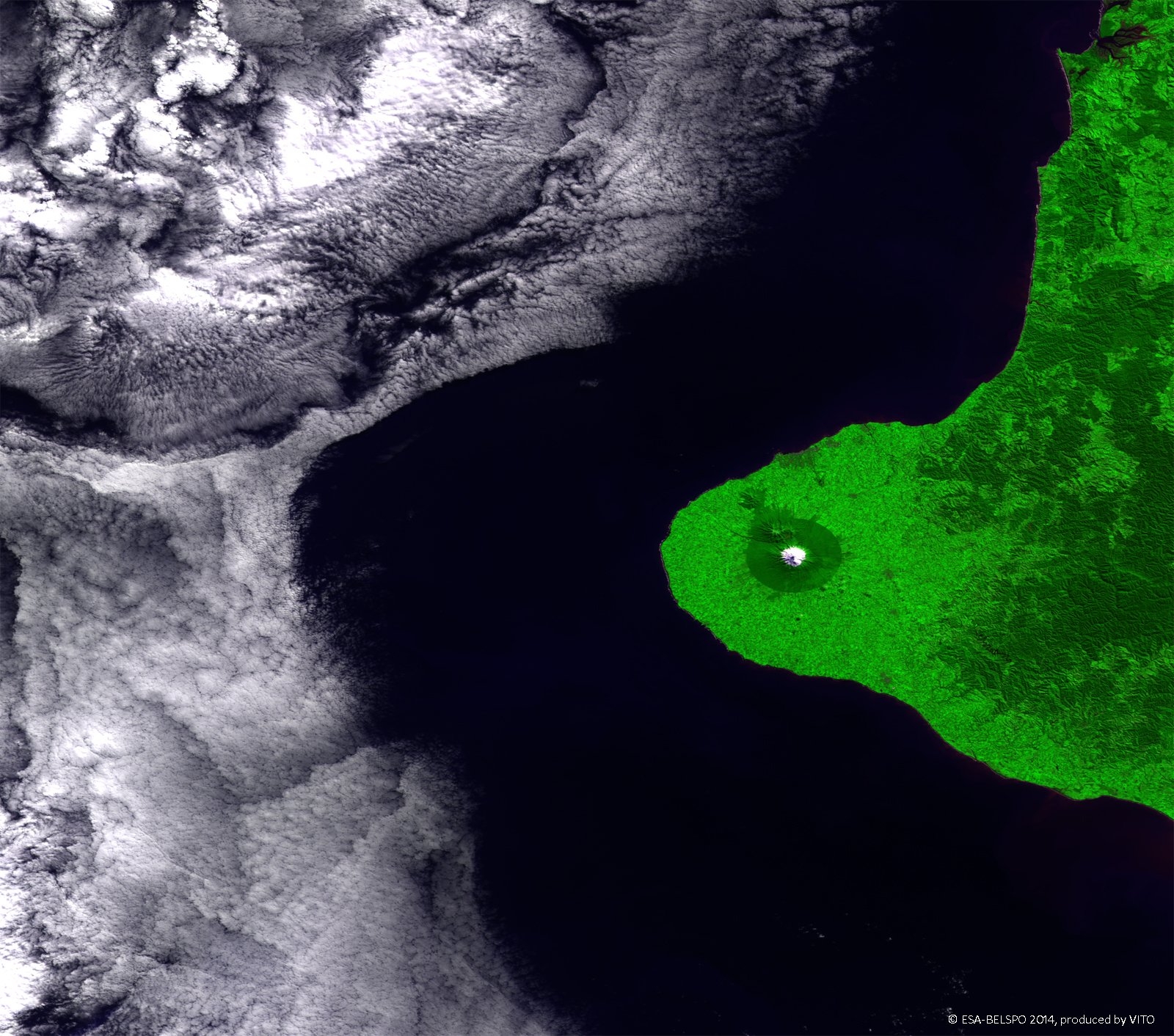
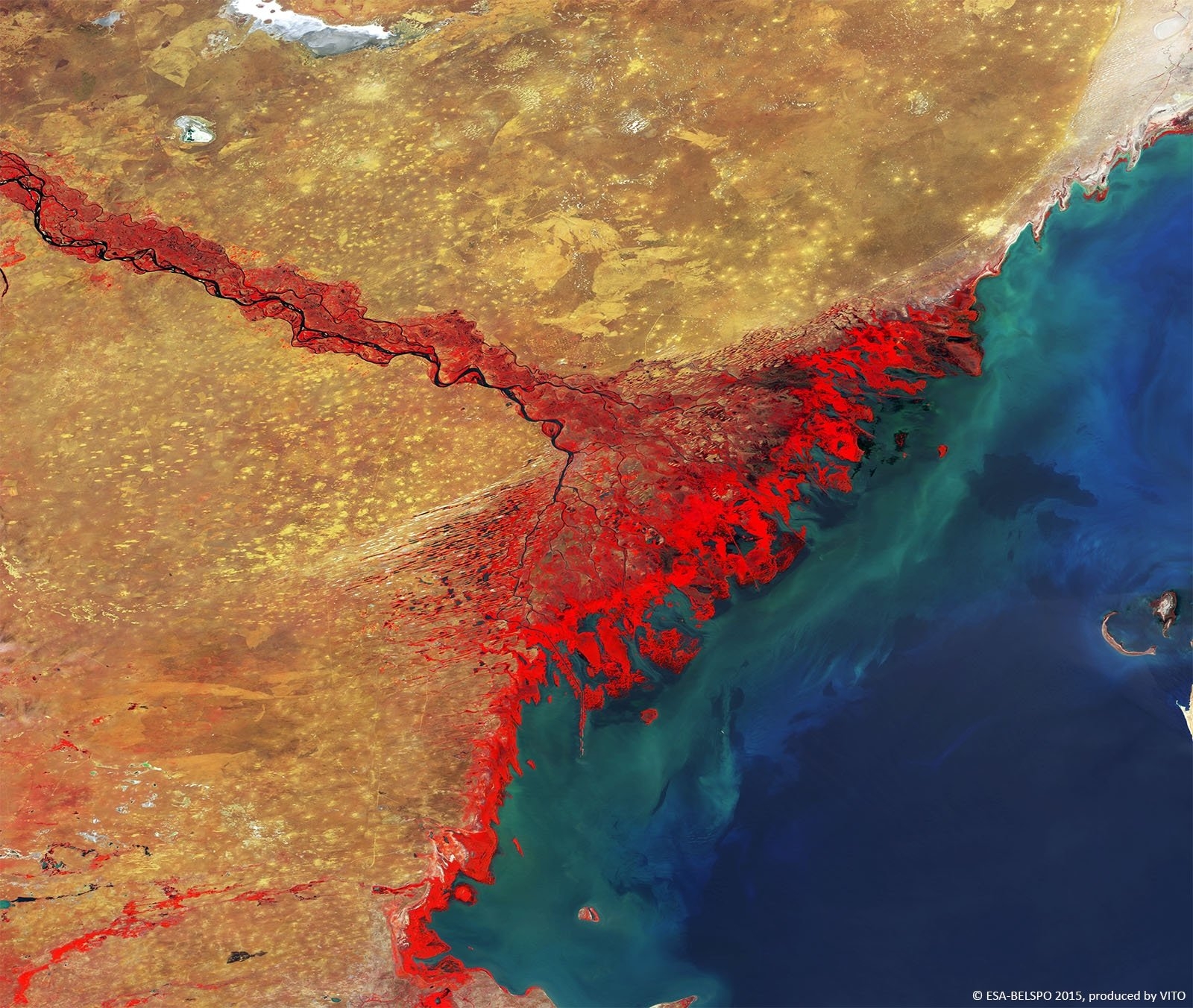
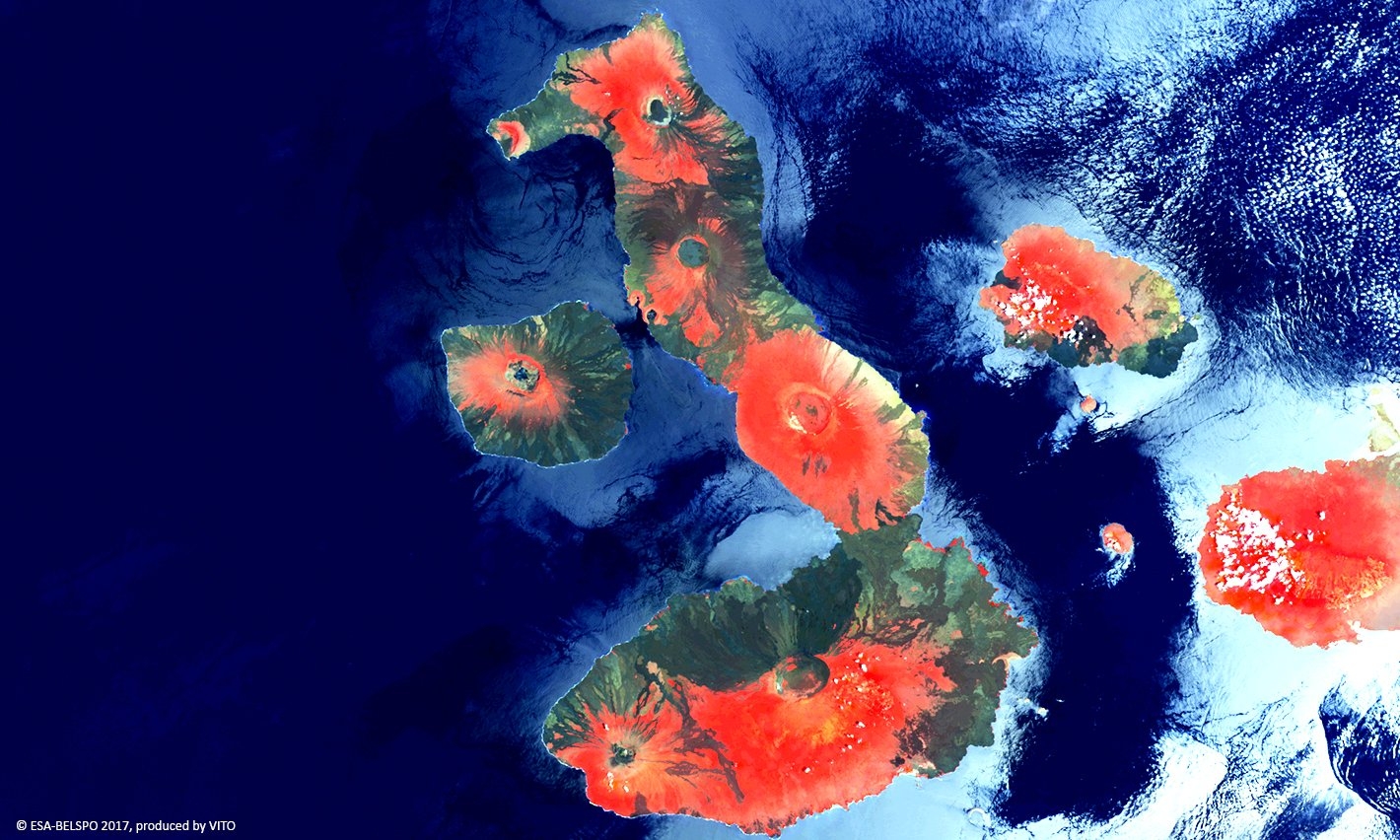
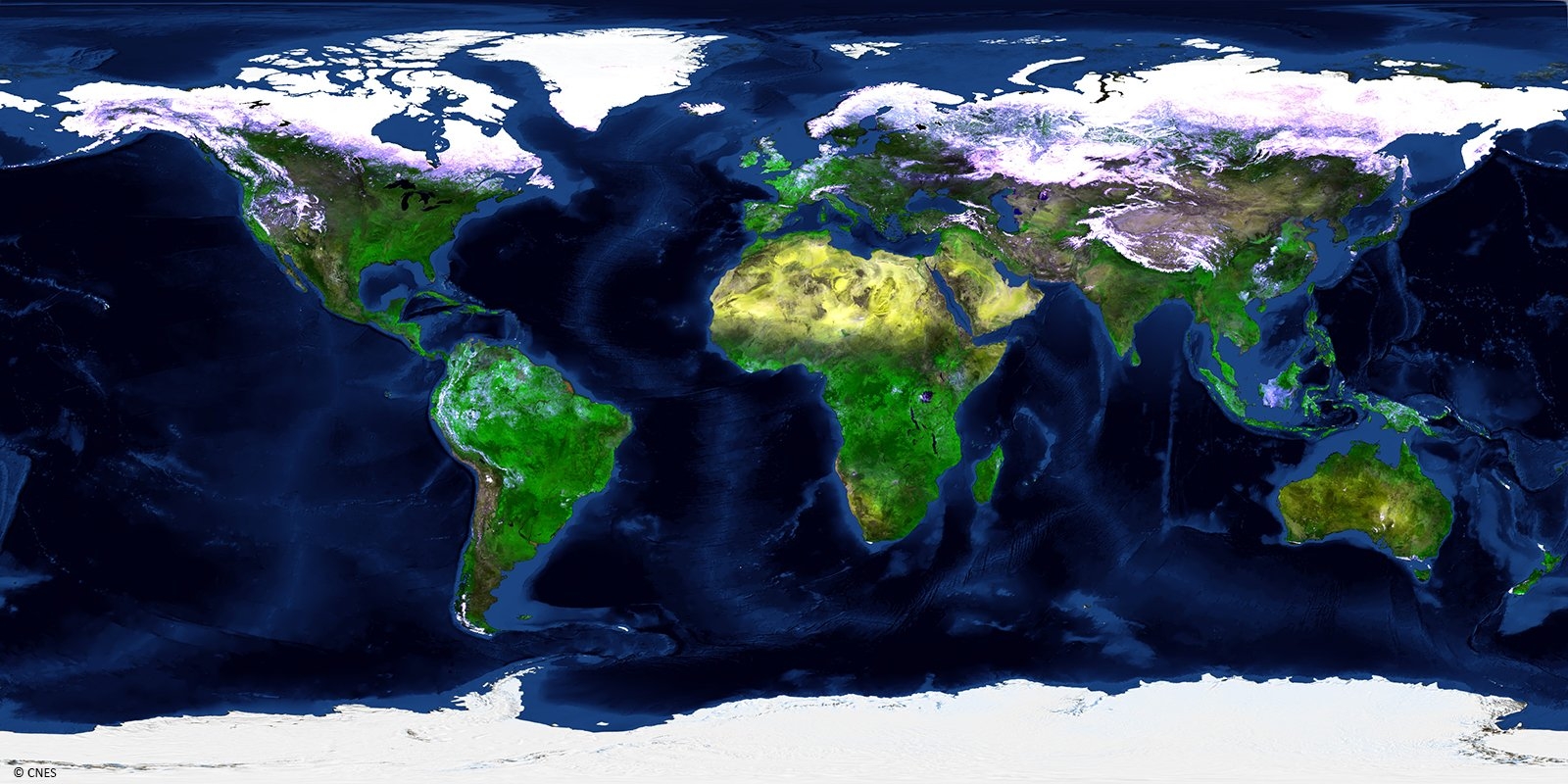
PROBA-V is an ESA microsatellite from the PROBA family (Project for On-Board Autonomy with V standing for VEGETATION). It has been developed mainly by a Belgian consortium (QinetiQ Space, OIP, VITO) with a small contribution from among others Luxembourg and Canada, through the GSTP Programme of ESA.
A follow-up to the 17-year SPOT-VEGETATION mission
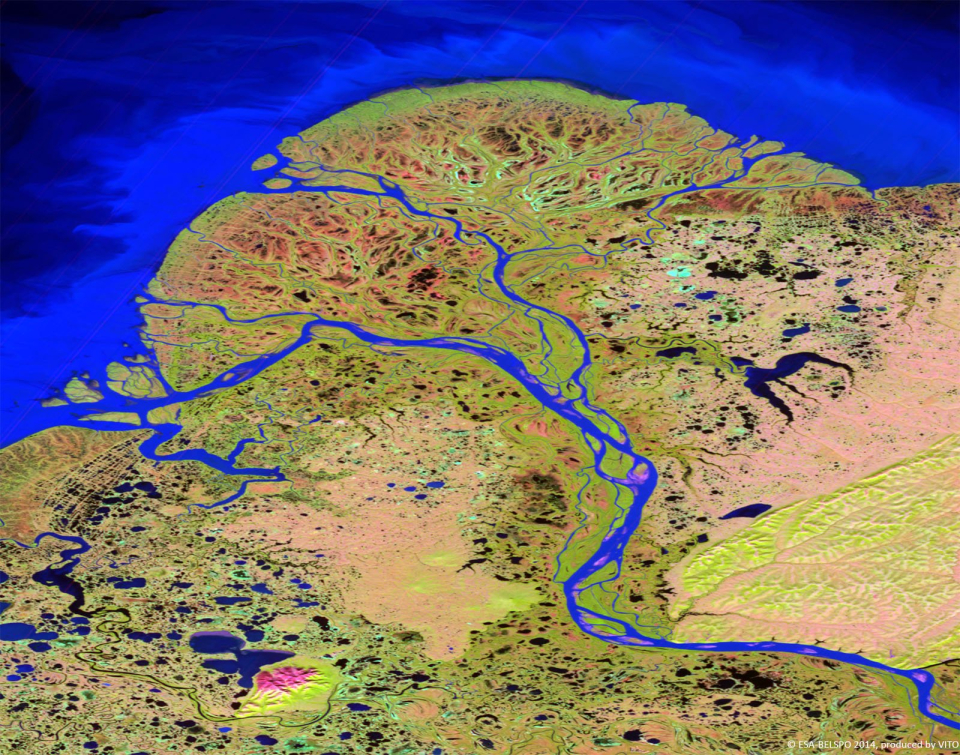

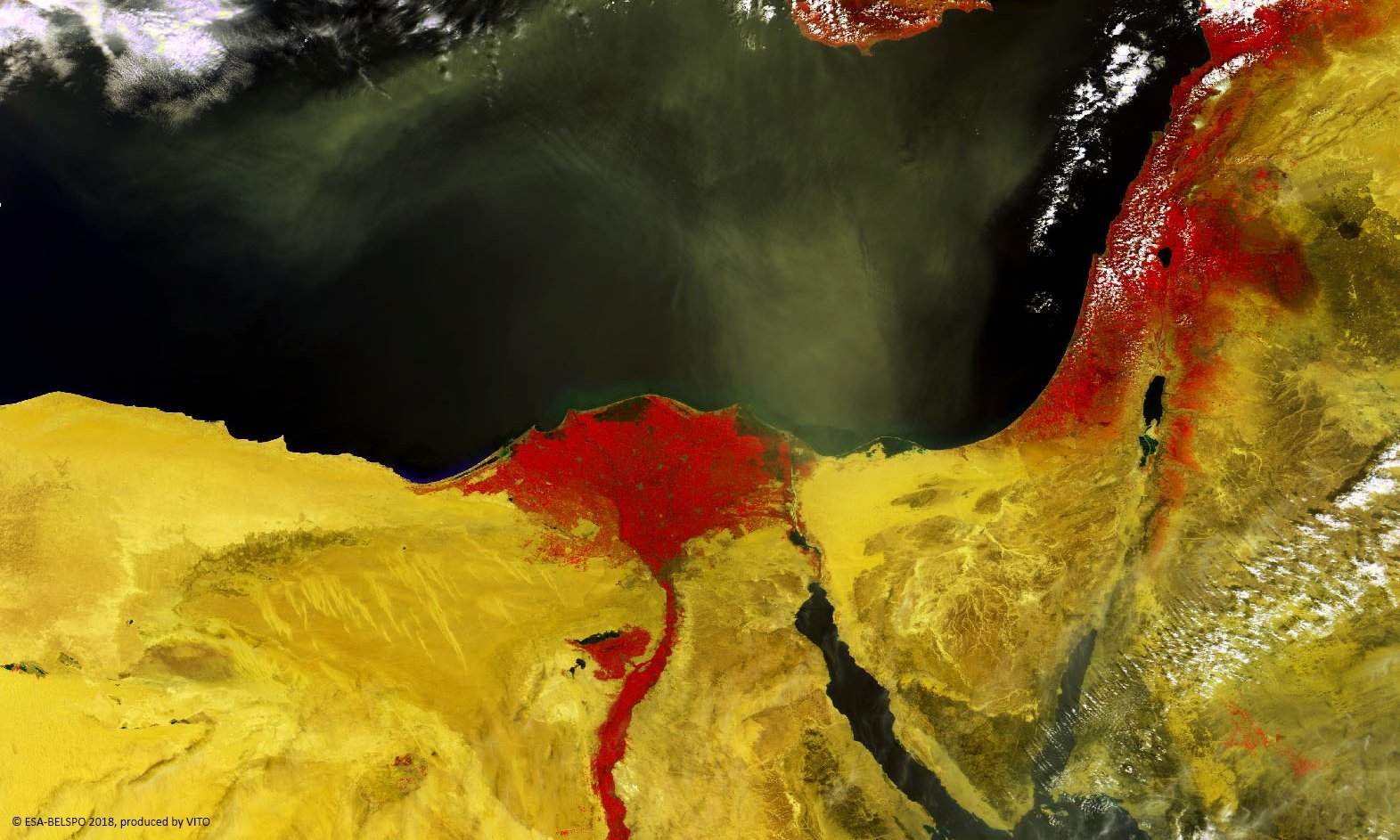
PROBA-V’s spectral channels are therefore similar to those of the SPOT VEGETATION instrument. However, benefiting from the technological developments since the SPOT-VEGETATION launch in 1998, PROBA-V spatial resolution now goes up to 100 m instead of 1 km.
PROBA-V was launched on 7 May 2013 and is planned to stay in operation until 30 June 2020. The operations are jointly managed through ESA’s Earthwatch Programme and the Belgian CVB programme. From 1 July 2020 until 30 October 2021, PROBA-V will keep acquiring data over the European and African continent, but in an 'experimental' mode.
The PROBA-V data are processed and archived by CVB and can be accessed via the Product Distribution Portal.
Derived biophysical products are produced by the Copernicus Global Land Service.